Introduction
Mexican veggies have always played a central role in the country’s culinary tradition. Not only do they provide flavor, texture, and nutrition to countless dishes, but they also reflect the diversity of Mexico’s unique agricultural landscape. Hearty soups, refreshing salads, and street tacos all feature these vegetables, telling a story that connects the past with the present. By actively linking Mexico’s culinary history with its modern cuisine, these ingredients bridge generations and keep traditions alive. Moreover, their widespread use combines indigenous crops with influences from other parts of the world, making them both versatile and culturally significant.
Historical Significance
The story of Mexican vegetables stretches back to ancient civilizations like the Aztecs and Mayans, where they were far more than just food. Corn, squash, and beans—fondly referred to as the “Three Sisters”—formed the backbone of their diet and sustained entire populations. In addition, these indigenous crops symbolized life, prosperity, and even spirituality in Mexican culture. For example, people in ancient civilizations considered corn sacred and central to their mythologies. Thus, these vegetables deeply intertwined with their way of life.
Cultural Impact
Fast-forward to today, and Mexican veggies remain an integral part of the country’s identity. From vibrant street food stalls to upscale gourmet restaurants, they shine in recipes that celebrate their natural flavors and nutritional value. Furthermore, they serve as bridges to the past, keeping ancient traditions alive in a modern culinary world. For instance, the practice of preparing tamales or roasting chayote reflects techniques that have been passed down through generations. As a result, these vegetables hold a special place in both the kitchens and hearts of the Mexican people.
Overview of Common Mexican Vegetables
The world of Mexican veggies is vast and incredibly diverse. Not only does it include native varieties, but it also incorporates crops that were introduced during colonial times. Let’s take a closer look at these delicious and versatile ingredients that have stood the test of time.
Native Varieties
Indigenous vegetables like chayote, nopales, and tomatillos continue to thrive in Mexican agriculture. Because of their unique flavors and versatility, they are still widely cultivated and beloved across the country. For example, nopales (cactus pads) are enjoyed in tacos, salads, and even scrambled eggs. Meanwhile, tomatillos are the stars of tangy green salsas that accompany almost every meal. In fact, these staples have remained virtually unchanged since the days of pre-Hispanic Mexico, preserving a deep connection to the land and its history.
Introduced Species
Following European contact, new crops like carrots, onions, and garlic made their way into Mexican cuisine. Over time, these non-native vegetables became indispensable, blending seamlessly with the country’s indigenous produce. For example, onions and garlic are now the foundation of countless dishes, providing aromatic bases for stews, sauces, and marinades. Additionally, these introduced species have expanded the range of flavors and techniques in Mexican cooking, proving how adaptable and evolving the cuisine truly is. In short, the combination of native and introduced vegetables has created a vibrant culinary tradition that continues to evolve while honoring its roots.
Part 2: Native Mexican Vegetables
Indigenous Vegetables of Mexico
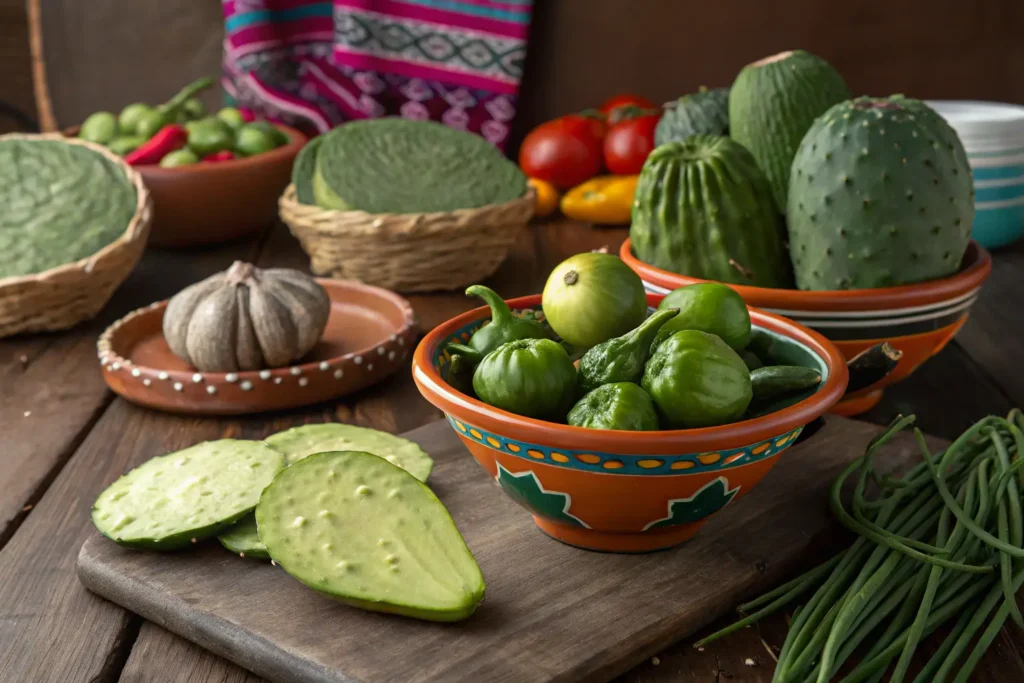

Mexico is home to a treasure trove of indigenous vegetables, many of which have been staples for centuries. These unique crops are not only packed with nutrients but also embody the flavors and history of Mexican cuisine. From the versatile nopales to the tangy tomatillos, native Mexican veggies have defined the culinary identity of the region and are celebrated globally for their rich taste and cultural significance.
Nopales (Cactus Pads)
Nutritional Benefits
Nopales are a powerhouse of nutrition. They’re low in calories but rich in fiber, which supports healthy digestion. Packed with antioxidants, vitamins A and C, and essential minerals like calcium and magnesium, nopales are excellent for managing blood sugar levels and promoting heart health.
Culinary Uses
Nopales are incredibly versatile. They’re often grilled, sautéed, or boiled, and their slightly tangy flavor makes them a popular ingredient in salads, tacos, and soups. Whether served as a side dish or a main ingredient, nopales bring a fresh, zesty twist to any meal.
Chayote (Mexican Squash)
Nutritional Benefits
Chayote, often called Mexican squash, is brimming with nutrients. It’s a great source of vitamin C, potassium, and folate, making it ideal for boosting immunity and supporting overall health. Plus, its low calorie and high water content make it perfect for weight management.
Culinary Uses
Chayote has a mild, crisp flavor that works well in various dishes. It can be steamed, boiled, or stir-fried and is often used in soups and stews. For a refreshing twist, thinly sliced chayote can also be eaten raw in salads, drizzled with lime juice.
Tomatillos (Husk Tomatoes)
Nutritional Benefits
Tomatillos are rich in vitamins C and K, as well as antioxidants that promote healthy skin and immune function. They also contain compounds that may help regulate blood pressure and cholesterol levels, making them a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Culinary Uses
Tomatillos are best known for their role in salsa verde, where their tart flavor adds depth and brightness. They can also be roasted, grilled, or stewed to enhance their natural sweetness. Whether used in sauces, soups, or casseroles, tomatillos are a must-have in Mexican cuisine.
Part 3: Commonly Used Vegetables in Mexican Dishes
Staples in Mexican Cooking
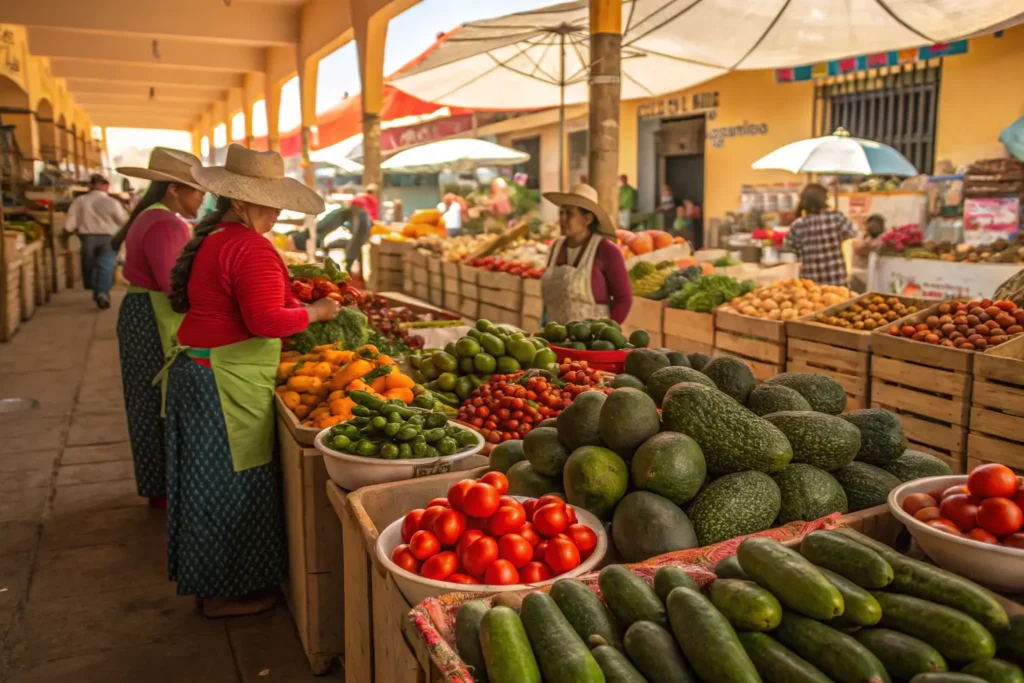

Some vegetables are so integral to Mexican dishes that they’ve become synonymous with the cuisine itself. From the juicy sweetness of tomatoes to the creamy richness of avocados, these staples elevate everything from salsas to stews. Let’s explore some of the most common vegetables used in Mexican cooking.
Tomatoes
Role in Salsas and Sauces
Tomatoes are the backbone of many iconic Mexican dishes. They’re the main ingredient in salsas, moles, and enchilada sauces, providing the perfect balance of acidity and sweetness. Roasting or charring tomatoes adds a smoky depth that enhances any dish.
Health Benefits
Bursting with vitamins A and C, tomatoes are a great source of lycopene, a powerful antioxidant that supports heart health and reduces inflammation. Their versatility makes them both delicious and nutritious.
Avocados
Guacamole and Beyond
Avocados are most famous for guacamole, but their creamy texture makes them ideal for salads, tacos, and even smoothies. Mashed, sliced, or diced, they bring a luscious richness to every bite.
Nutritional Profile
Avocados are packed with healthy monounsaturated fats, which are great for heart health. They’re also loaded with potassium, fiber, and vitamins E and K, making them a nutrient-dense superfood.
Peppers (Chiles)
Variety and Heat Levels
From mild poblanos to fiery habaneros, peppers are a cornerstone of Mexican cooking. Their heat varies widely, allowing chefs to create everything from subtle dishes to bold, spicy creations.
Uses in Traditional Recipes
Peppers are used in countless ways: dried and ground for spice blends, roasted for sauces, or stuffed with cheese and meats. They add complexity and vibrancy to dishes like chile rellenos and salsas.
Corn (Maize)
Foundation of Mexican Cuisine
Corn is the heart of Mexican cuisine. Ground into masa for tortillas and tamales or served fresh in elotes (grilled corn on the cob), this ancient crop is truly versatile.
Nutritional Importance
Corn provides essential nutrients like fiber, B vitamins, and magnesium. Its slow-digesting carbs offer sustained energy, making it a dietary staple for centuries.
Part 4: Regional Vegetables and Their Culinary Uses
Regional Specialties
The unique geography and climate of Mexico have given rise to a dazzling array of regional vegetables. Each area of the country has its own prized ingredients, which have become central to traditional dishes and culinary practices. From the nutrient-rich huauzontle to the crisp and refreshing jicama, these vegetables reflect the agricultural diversity of Mexico and its deep-rooted connection to the land. Let’s dive into some of these regional treasures and discover their culinary uses.
Huauzontle (Mexican Broccoli)
Traditional Dishes
Huauzontle, a lesser-known relative of quinoa, is often used in traditional dishes such as tortas de huauzontle, where the clusters of green buds are coated in batter, fried, and simmered in a tomato-based sauce. Its mild, slightly earthy flavor pairs well with a variety of seasonings and sauces, making it a versatile ingredient.
Nutritional Information
Rich in vitamins A and C, huauzontle is also a good source of iron and calcium. Its high fiber content supports digestive health, while its antioxidant properties help boost the immune system.
Jicama (Mexican Turnip)
Popular Preparations
Jicama is often enjoyed raw in salads, slaws, or as a refreshing snack. Thinly sliced and sprinkled with lime juice, chili powder, and salt, it becomes a crunchy and flavorful treat. Its crisp texture also makes it an excellent addition to tacos and fruit cups.
Health Benefits
Jicama is low in calories and high in water content, making it hydrating and great for weight management. It’s also a rich source of inulin, a prebiotic fiber that promotes gut health, as well as vitamin C, which supports a strong immune system.
Epazote (Herb)
Flavor Profile
Epazote has a distinctive, pungent flavor that’s slightly bitter with hints of mint and anise. It’s a bold herb that’s often used sparingly to enhance the flavor of dishes without overwhelming them.
Culinary Applications
Traditionally, epazote is added to dishes like black beans, tamales, and quesadillas to reduce their heaviness and aid digestion. Its unique aroma and flavor make it a popular seasoning in regional Mexican cooking.
Purslane (Verdolagas)
Traditional Recipes
Purslane, or verdolagas, is a common ingredient in stews and sautés. One popular dish is cerdo con verdolagas, where the succulent leaves are cooked with pork and green tomatillo sauce. Its slightly tangy taste enhances the dish’s flavor.
Nutritional Value
Purslane is a nutritional powerhouse, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A and C, and minerals like magnesium and potassium. Its high antioxidant content makes it an excellent choice for promoting overall health.
Part 5: Nutritional Benefits of Mexican Vegetables
Health Advantages
Mexican vegetables are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients that support a healthy lifestyle. From vitamins and minerals to fiber and antioxidants, these vegetables offer a wide range of health benefits that go beyond satisfying your taste buds.
Vitamins and Minerals
Contribution to Diet
Many Mexican veggies are rich in key vitamins such as A, C, and K, which promote eye health, boost immunity, and support bone health. They’re also a great source of essential minerals like potassium, magnesium, and calcium, which help regulate blood pressure and maintain strong bones.
Disease Prevention
The high vitamin content of Mexican vegetables plays a role in preventing chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. Vitamin C, for example, acts as a powerful antioxidant that reduces oxidative stress and strengthens the immune system.
Fiber Content
Digestive Health
Fiber-rich vegetables like nopales and jicama support healthy digestion by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. They also encourage the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which is essential for overall health.
Weight Management
Vegetables with high fiber content provide a sense of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake. This makes them an excellent choice for those looking to maintain or lose weight while enjoying nutritious and satisfying meals.
Antioxidant Properties
Role in Reducing Inflammation
Many Mexican veggies, such as tomatillos and peppers, are loaded with antioxidants that help fight inflammation. These compounds reduce the risk of chronic conditions like arthritis and cardiovascular diseases.
Cancer Prevention
The antioxidants found in Mexican vegetables—such as lycopene in tomatoes—help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. This process lowers the risk of developing certain cancers by protecting cells from damage.
Part 6: Seasonal Availability and Selection Tips
Choosing the Best Mexican Vegetables
Seasonality plays a significant role in the quality and flavor of Mexican veggies. Selecting vegetables at their peak ensures you get the freshest and most nutrient-rich produce. Here’s how to choose the best vegetables throughout the year and keep them fresh for longer.
Seasonal Guide
Spring and Summer Varieties
During spring and summer, vegetables like tomatillos, chayote, and fresh corn are at their peak. These veggies thrive in the warmer months and bring vibrant flavors to dishes like salads and salsas.
Fall and Winter Varieties
Cooler months are perfect for heartier vegetables like nopales and huauzontle. Their robust flavors and textures make them ideal for warm, comforting stews and casseroles.
Tips for Selecting Fresh Produce
Signs of Freshness
Look for bright, vibrant colors and firm textures when selecting vegetables. Avoid produce with blemishes, soft spots, or signs of wilting, as these indicate reduced freshness.
Storage Recommendations
Store vegetables like tomatillos and peppers in a cool, dry place or refrigerate them to extend their shelf life. Leafy herbs like epazote should be wrapped in a damp paper towel and kept in the fridge to maintain freshness.
Part 7: Cooking Techniques for Mexican Vegetables
Preparing Mexican Vegetables
Cooking Mexican veggies is an art that enhances their natural flavors while preserving their nutritional value. From grilling to sautéing, each technique brings out a unique taste and texture. Let’s explore the best ways to prepare these vibrant vegetables for a variety of delicious dishes.
Grilling and Roasting
Enhancing Flavors
Grilling and roasting intensify the natural sweetness of vegetables like tomatoes, peppers, and chayote. The smoky char adds depth, making these techniques ideal for dishes like roasted tomatillo salsa or grilled nopales.
Suitable Vegetables
Vegetables with firm textures, such as chayote, peppers, and huauzontle, are perfect for grilling or roasting. Their ability to hold up to high heat ensures they develop a deliciously caramelized surface.
Boiling and Steaming
Preserving Nutrients
Boiling and steaming are gentle cooking methods that retain the nutrients in delicate vegetables like purslane and jicama. These techniques keep the veggies tender while locking in their natural flavors.
Ideal Choices
Leafy vegetables like epazote and tender veggies like chayote are ideal for boiling or steaming. Steamed chayote cubes, for example, make a fantastic base for fresh salads or side dishes.
Sautéing and Stir-Frying
Quick Cooking Methods
Sautéing and stir-frying are quick and efficient, allowing vegetables to retain their crunch and vibrant colors. Adding a touch of oil and spices enhances their flavor while keeping the texture intact.
Best Vegetables for This Technique
Vegetables like tomatoes, poblanos, and nopales are perfect for sautéing. They cook quickly and absorb spices beautifully, making them ideal for tacos, burritos, or stir-fry bowls.
Raw Preparations
Salads and Salsas
Raw Mexican veggies are a staple in salads and salsas, where their natural flavors shine. Thinly sliced jicama, diced tomatillos, and fresh avocados combine to create refreshing, crunchy dishes.
Health Benefits
Raw vegetables retain all their vitamins and minerals, offering maximum health benefits. Dishes like nopalitos salad or salsa verde pack a nutritional punch while delivering bold, fresh flavors.
Part 8: Traditional Mexican Vegetable Dishes
Classic Recipes Featuring Vegetables
Traditional Mexican dishes celebrate the country’s incredible variety of vegetables, using them as the star ingredients. From hearty stews to refreshing salads, these recipes honor both flavor and tradition.
Calabacitas con Elote (Zucchini with Corn)
Recipe Overview
Calabacitas con elote is a comforting dish made with tender zucchini, sweet corn, and a medley of spices. Often topped with cheese, it’s a simple yet flavorful recipe that pairs beautifully with rice or tortillas.
Cultural Significance
This dish has its roots in rural Mexican kitchens, where seasonal vegetables were used to create wholesome meals. It reflects the ingenuity of combining simple ingredients to produce something extraordinary.
Rajas con Crema (Poblano Strips with Cream)
Preparation Method
Rajas con crema features roasted poblano strips cooked in a creamy sauce with onions and cheese. The roasting process enhances the peppers’ smoky flavor, making this dish a crowd favorite.
Serving Suggestions
This dish is traditionally served with warm tortillas, making it perfect for tacos or as a side dish to grilled meats. Its creamy texture complements the heat of the poblano peppers.
Sopa de Verduras (Vegetable Soup)
Common Ingredients
Sopa de verduras is a hearty vegetable soup made with tomatoes, chayote, carrots, and purslane. Herbs like epazote add a unique depth of flavor, making it a satisfying meal.
Nutritional Benefits
This soup is packed with vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants, making it a nourishing choice for any season. It’s a comforting way to enjoy the health benefits of Mexican veggies.
Nopalitos Salad
Preparation Tips
Nopalitos salad features tender cactus pads, diced tomatoes, onions, and a tangy lime dressing. Blanching the nopales beforehand removes their natural slime, ensuring a clean and crisp texture.
Flavor Profile
The salad is refreshing and slightly tangy, with a balance of savory and citrusy flavors. It’s an excellent accompaniment to grilled meats or as a light main dish.
Part 9: Incorporating Mexican Vegetables into Modern Cuisine
Fusion and Contemporary Uses
While rooted in tradition, Mexican veggies have also found their way into modern culinary trends. Chefs worldwide are using these ingredients to create innovative dishes that blend traditional flavors with contemporary techniques.
Mexican-Inspired Salads
Creative Combinations
Modern Mexican-inspired salads combine ingredients like avocado, purslane, and jicama with unique dressings like honey-lime vinaigrette. Adding grilled proteins or quinoa can elevate these salads into complete meals.
Dressing Ideas
Dressings made with roasted tomatillos, blended with garlic and lime juice, add a burst of flavor to any salad. Creamy avocado-based dressings are also a popular choice for creating vibrant dishes.
Vegetable Tacos and Wraps
Innovative Fillings
Vegetable tacos feature roasted nopales, sautéed peppers, or grilled chayote. Combining these with beans, cheese, or even quinoa provides a satisfying twist on traditional tacos.
Healthier Alternatives
Using lettuce leaves or whole-grain tortillas instead of traditional wraps creates a healthier, low-carb alternative. Filling these with fresh veggies and light sauces makes for a nutritious yet flavorful meal.
Conclusion
Mexican vegetables are much more than simple ingredients; they are a vibrant expression of the country’s history, culture, and culinary ingenuity. From ancient crops like corn, squash, and beans—the “Three Sisters”—to modern staples like avocados, tomatoes, and peppers, these vegetables have shaped and enriched Mexican cuisine over centuries. Their versatility shines in every dish, whether grilled, sautéed, or enjoyed raw in salsas and salads.
Moreover, these veggies offer remarkable health benefits, packed with vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants that promote wellness while delighting the palate. By understanding their seasonal availability and unique cooking techniques, you can not only enjoy their incredible flavors but also honor the deep cultural roots they represent.
Incorporating Mexican veggies into your cooking means more than just enhancing your meals—it means embracing a rich culinary tradition that connects the past with the present. So, whether you’re roasting tomatillos, steaming chayote, or adding nopales to a fresh salad, remember that you’re celebrating a legacy of flavor, health, and heritage. Let these vibrant vegetables transform your kitchen and inspire your next meal!
External Link: https://www.isabeleats.com/mexican-roasted-vegetables/